PMOS / P-Channel MOSFET
Logic Level PMOS
Summary
Orient the P-Channel MOSFET (PMOS) in a circuit so that the drain pin (D) is connected to the supply positive, and the source pin (S) is connected to the load positive. Voltage up to the Vdss Drain-Source Voltage and current up to the lesser of the Id Drain Current and the Is Maximum Continuous Drain-Source Diode Forward Current will be conducted from the drain to the source when the PMOS gate pin sees a voltage more negative than the 'On Characteristic' Vgs(th) Gate Threshold Voltage maximum value. Reverse voltages greater than the Vsd Drain-Source Diode Forward Voltage value (the more negative value when looking at the difference of Vg and Vd) will be blocked by the built-in body diode. Use it to add reverse polarity protection, or to switch high side loads up to 60V @ 20 A.
Detailed Explanation
Pay careful attention to the orientation of the PMOS in a circuit. A PMOS has a body diode that conducts current under forward-bias conditions (current traveling from the drain to the source).
The FQP27P06 PMOS for example, has a maximum Drain-Source Diode Forward Voltage (Vsd) of -4 V, and a Maximum Continuous Drain-Source Diode Forward Current of -27 A. Any reverse voltage more negative than -4 V won't be conducted from the drain to the source (source +, drain -) due to this diode. For example, in a reverse polarity situation where the drain is connected to ground and the source is connected to +4 VDC or more (properly stimulating the PMOS gate), the result will be no current flow between the PMOS source and drain pins (but it would for +3.3 V at the source).
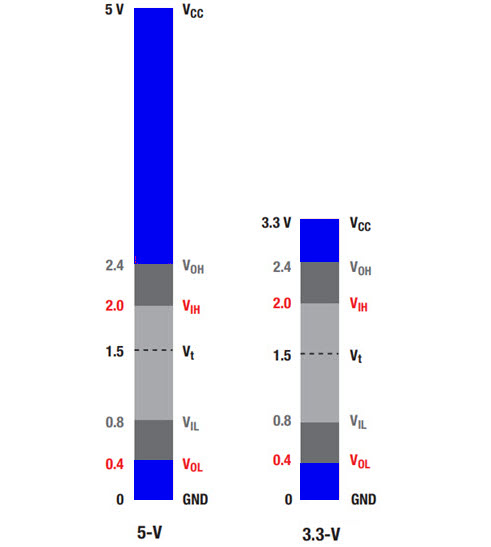
The FQP27P06 PMOS Vgs(th) gate threshold voltage is rated at -2.0 minimum and -4.0 V maximum. This means that the difference of the gate voltage and the drain must be more negative than -4.0 V in order for the PMOS to conduct current flow from the drain to the source. For a 5 VDC power supply with the + connected to the PMOS drain and a 10 kOhm resistor pulling the PMOS gate to ground, the difference of the gate voltage relative to the drain would be Vg - Vd = 0.0 V - 4.99 V = -4.99 V (-4.99 V because of the 10 kOhm resistor and the small 0.07 ohm resistance of the PMOS in the circuit). Note that since the gate threshold voltage is -2.0 V minimum, and -4.0 V maximum, a voltage of -3.3V at the gate is not recommended for reliable stimulation of the gate.
The TP2535 has a Vgs th - Gate-Source Threshold Voltage of 2.4V and therefore can provide reverse polarity protection down to 3.3 V.
Reverse Polarity Protection Application Example
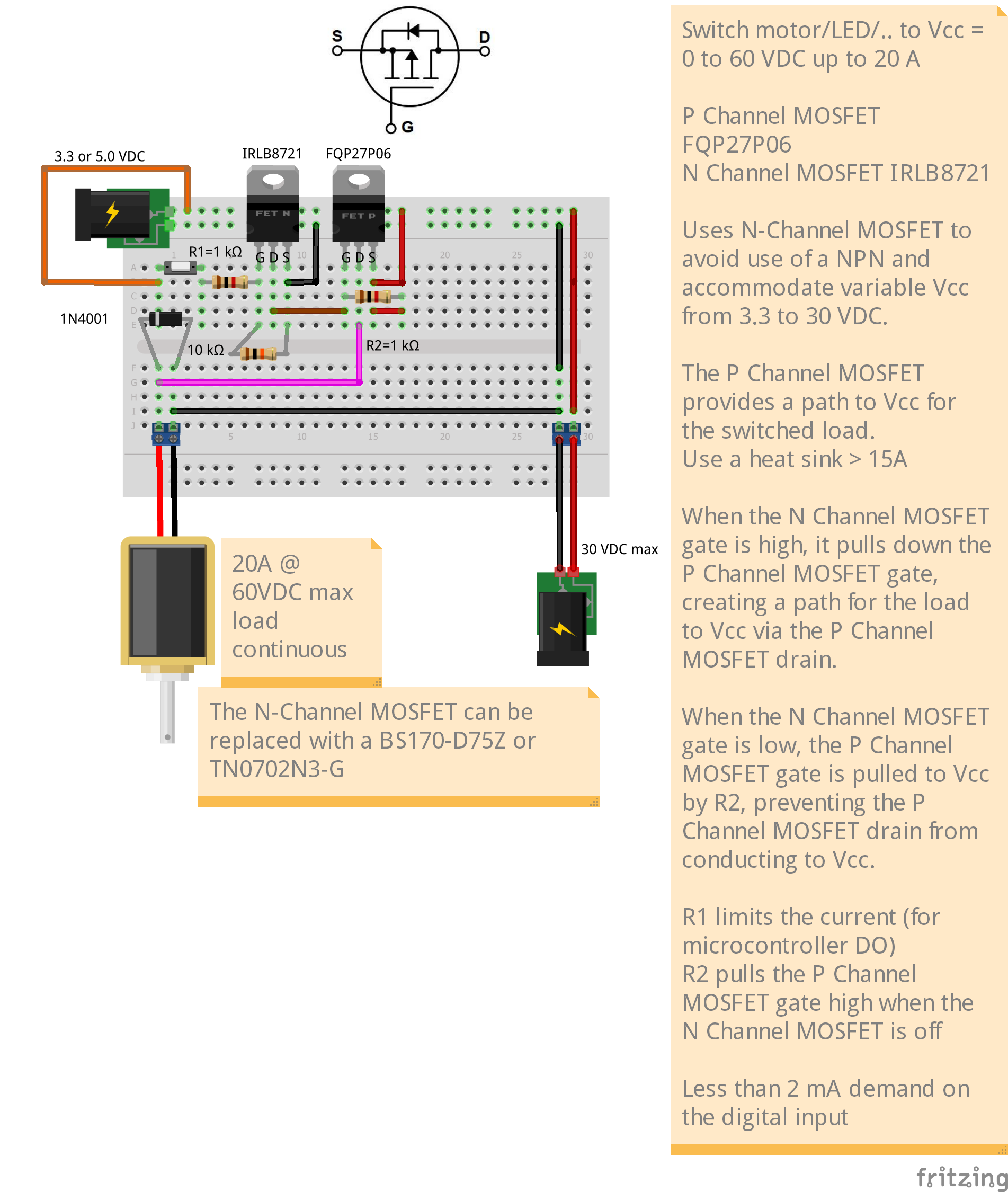
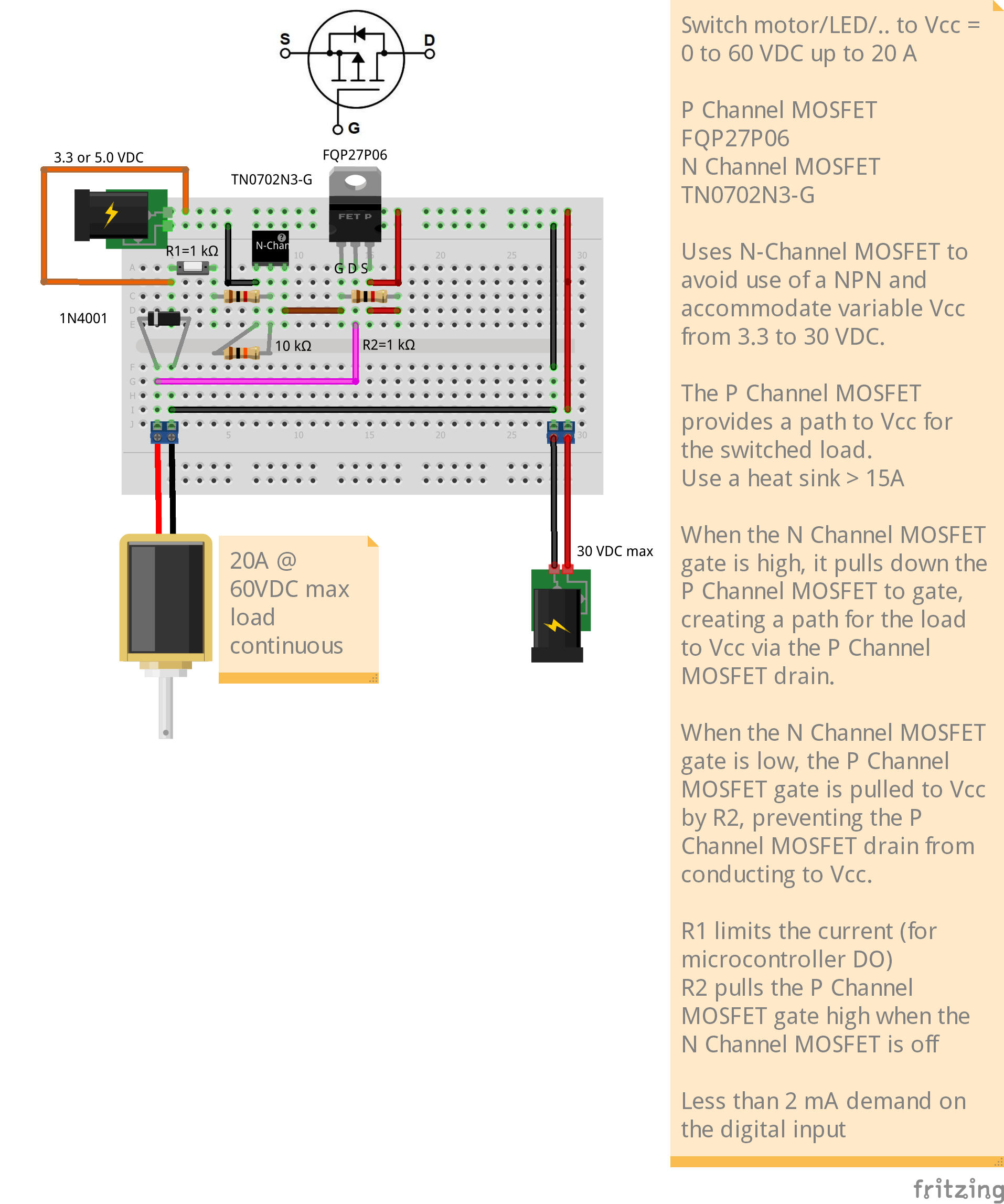
High Side Switching Application
The two circuits below us a N-Channel MOSFET (NMOS) to control the gate of a P-Channel MOSFET (PMOS). The gate on the NMOS is controled by a 3.3 or 5V logic microcontroller and only demands about 2 mA of current from the MCU digital output. The PMOS can switch up to 60 VDC @ 20 A (with proper heat sink).
Do you need help developing or customizing a IoT product for your needs? Send me an email requesting a free one hour phone / web share consultation.
The information presented on this website is for the author's use only. Use of this information by anyone other than the author is offered as guidelines and non-professional advice only. No liability is assumed by the author or this web site.
.jpg)
_bb.png)











.png)
.png)






.png)
.png)



.png)




.png)

.png)
.jpg)

.png)



.png)



.png)